There’s a lot of jargon and types of marketing strategies floating around in marketing, and sometimes it can get confusing –– especially when we talk about inbound and outbound marketing.
We're here to clarify everything and make it as simple as possible for you to understand, starting with account based marketing (ABM) and inbound marketing. So, what do they mean?
What is account based marketing?
ABM is an outbound marketing process that targets and engages specific high-value customers identified and pre-selected by sales and marketing specialists rather than targeting a broad audience.
The special thing about this is not every customer is seen as an individual entity. Instead, companies are viewed as groups of buyers called accounts. A company, or account, is then treated as an individual buyer whose plans and interests marketing efforts are tailored.
This marketing strategy aims to strengthen long-term business relationships and achieve constant growth for your company. ABM focuses on restoring personal relationships between sellers and buyers in a world increasingly driven by detachment.
What is inbound marketing?
Inbound marketing seeks to attract customers with helpful content distributed through a high-converting website, valuable content or engaging social media activity — among other channels.
Inbound marketing is considered standard nowadays as it prioritises a customer's desires and requirements first, providing valuable content to help them solve their problems.
It's a broader strategy than ABM but one that works for companies across all sectors with various target audiences.
The core aspects and strategies of inbound and account based marketing
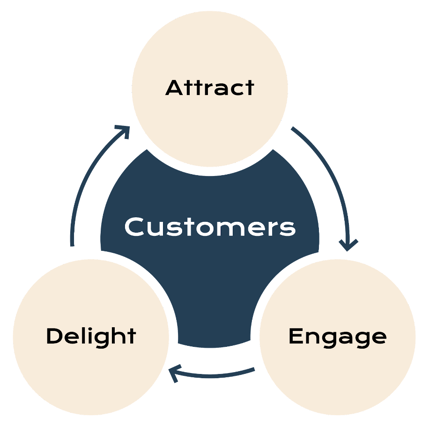
The classic inbound marketing model is based on the flywheel model, which emphasises the ongoing relationship between the customer and the business to turn customers into promoters.
This helps attract new customers through word-of-mouth referrals and can be split into three phases: Attract, engage and delight.
ABM's strategy doesn’t involve capturing customers through large-scale campaigns. Instead, targeted marketing campaigns are created for the accounts, tailored to specific companies and their decision-makers. The intention is to build mutual trust and long-term business relationships.
A core aspect of ABM can be imagined as a reverse funnel starting with a narrow focus on high-value target accounts and expanding over time as relationships deepen.
Here's how the ABM reverse funnel typically works:
-
Identifying target accounts: Instead of casting a wide net to attract leads, ABM begins by identifying a select group of high-value target accounts that align with the company's strategic objectives. These accounts are chosen based on revenue potential, industry fit and likelihood of success
-
Personalising marketing efforts: Once target accounts are identified, marketing efforts are personalised and tailored specifically to address the unique needs, challenges and interests of each account. This may involve creating customised content, messaging and campaigns designed to resonate with key decision-makers within the target accounts
-
Engaging key decision-makers: With a narrow focus on target accounts, sales and marketing teams work closely together to engage key decision-makers and influencers within each account. This may involve personalised outreach, meetings, events and other tactics to build relationships and establish credibility
-
Expanding relationships and opportunities: As relationships with target accounts deepen and trust is established, the ABM reverse funnel begins to widen, allowing for expanding opportunities within existing accounts and identifying new potential opportunities. This may involve upselling and cross-selling additional products or services and leveraging referrals and introductions to other departments or divisions within the target accounts
-
Measuring and optimising performance: Throughout the ABM process, performance is continuously measured and optimised to ensure that resources are allocated effectively and results are maximised. Key metrics may include account engagement, pipeline growth, conversion rates and revenue generated from target accounts.
The similarities and differences between inbound marketing and ABM
| Similarities | Differences |
|
Customer-centric approach: Both ABM and Inbound marketing focus on understanding and addressing customers' needs, challenges and interests. They aim to provide value to customers rather than focusing solely on selling products or services. |
Audience focus: ABM targets a select group of high-value accounts or companies, typically in B2B (business-to-business) settings, whereas inbound marketing casts a wider net to attract a broader audience of potential customers. |
|
Personalisation: Both approaches emphasise the importance of personalisation in marketing efforts. Whether through tailored content, messaging or interactions, ABM and inbound marketing seek to deliver relevant and meaningful customer experiences. |
Approach: ABM is a targeted outbound marketing approach that involves personalised outreach and engagement with specific accounts, often involving collaboration between sales and marketing teams. In contrast, inbound marketing is an inbound approach that focuses on creating valuable content to attract and engage potential customers organically, often through channels like content marketing, social media and SEO. |
|
Relationship building: ABM and inbound marketing prioritise building strong, long-lasting customer relationships. They recognise the importance of engaging customers throughout their journey and providing exceptional experiences to foster loyalty and advocacy. |
Metrics and measurement: The metrics used to evaluate the success of ABM and inbound marketing can differ. ABM typically emphasises metrics related to account engagement, pipeline growth and revenue generated from target accounts. At the same time, inbound marketing may focus more on metrics like website traffic, lead generation and conversion rates. |
|
|
Timeline and engagement: ABM tends to have a shorter sales cycle with more focused, personalised engagement with target accounts, whereas inbound marketing may involve longer-term nurturing and relationship-building efforts with a broader audience over time. |
|
|
Resource allocation: ABM often requires more resources and coordination between sales and marketing teams to execute personalised campaigns for specific accounts, whereas inbound marketing may rely more on content creation and optimisation efforts to attract and engage a wider audience. |
The advantages and disadvantages of ABM
The advantages
- The greatest advantage of ABM lies in building good and lasting business relationships with customers, resulting in long-term gains for both sides. Short-term profit motives for one's own side aren't intended, as cooperation must be nurtured and coordinated from both sides to ensure success. Through ABM, the company gains authenticity
- ROI also becomes more measurable with ABM, as efforts can be clearly defined and measured through established success metrics. This ensures optimal tracking and reporting of the ROI
- Another advantage is that costs for broad marketing measures can be saved since campaigns are explicitly tailored to individual and specific customers or accounts.
The disadvantages
- ABM focuses on a select group of target accounts, meaning companies may miss out on opportunities with potential customers who fall outside their target account list
- ABM can be complex and challenging, especially for companies with large and diverse target account lists or those lacking the necessary technology and infrastructure for effective execution
- While personalisation is a key aspect of ABM, there’s a risk of over-personalisation, where messaging becomes too narrow or specific, potentially alienating other stakeholders within the target accounts
- While ABM can lead to shorter sales cycles for specific deals, larger and more complex deals may still require a longer sales cycle due to the need to build consensus and relationships among multiple stakeholders within the target accounts.
The advantages and disadvantages of inbound marketing
The advantages
-
Inbound marketing typically costs less than traditional outbound marketing methods like advertising. It relies on content creation and organic search traffic, which can lead to lower customer acquisition costs over time.
-
Attract and engage with a larger audience that is actively seeking information related to your products or services. This can result in higher-quality leads and better conversion rates.
-
By providing valuable and relevant content to your audience, inbound marketing helps build trust and establish your brand as an authority in your industry. This can lead to increased credibility and loyalty among your customers.
-
Unlike outbound marketing, which often provides short-term results, inbound marketing efforts can continue to generate leads and drive traffic to your website over time, resulting in sustainable long-term growth.
-
Inbound marketing allows you to track and measure the performance of your campaigns using various analytics tools. This enables you to gain insights into what works and what doesn't, allowing you to refine your strategies for better results.
The disadvantages
-
Inbound marketing requires consistent effort and investment in content creation, SEO, social media management and other activities. It can take time to see significant results, especially for new businesses or those with limited resources.
-
With the high popularity of inbound marketing, competition for attention and visibility online has become more intense. Standing out from the crowd and capturing the attention of your target audience can be challenging, especially in saturated markets.
-
Strategies rely heavily on search engine algorithms and social media algorithms to reach your audience. Changes to these algorithms can impact your visibility and reach, potentially affecting the effectiveness of your campaigns.
-
To maintain engagement and attract new leads, inbound marketing requires a steady stream of fresh and relevant content. This can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially for businesses with limited content creation capabilities.
-
While inbound marketing can deliver significant results over time, the outcomes may be unpredictable, especially in the early stages of implementation. It may take trial and error to find the right strategies that resonate with your target audience and drive desired outcomes.
Want to get started with inbound marketing?
Try this starter pack that uses templates we use for our own clients. Try them out for free here.
Which is better?
Inbound and account based marketing serve each other best as part of an interwoven marketing strategy. Both concepts have advantages and disadvantages. Although they’re often viewed as opposites, they have a similar goal and should be used in parallel.
Which concept makes more sense depends primarily on your company and the target groups. Inbound marketing and ABM are particularly worthwhile for companies in the B2B sector. ABM is also a good choice for niche markets, whereas inbound marketing is particularly profitable in large markets with broad target groups.
Avidly offers both ABM and inbound marketing capabilities. We’re your ideal contact for questions about these two topics. We work with potential clients to create customised inbound marketing service packages based on the client's revenue goals and available internal resources.
If you would like to learn more about this topic or obtain an offer, we’ll be happy to help. You can also arrange a free consultation with a live demo.




